Introduction to RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing
RKS.161.14.0414 is a specific model of slewing bearing known for its reliability and performance.Manufactured with precision engineering, RKS.161.14.0414 offers exceptional load-bearing capacity and rotational precision.Its design features make it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, contributing to enhanced efficiency and productivity.
Slewing bearings are specialized bearings designed to facilitate rotational movement. They are commonly used in heavy machinery and equipment to support axial and radial loads while enabling rotation. Slewing bearings play a crucial role in various applications, including cranes, excavators, wind turbines, and more.RKS.161.14.0414 holds significant importance in European industrial sectors due to its reliability and durability. European industries such as construction, renewable energy, and manufacturing rely on RKS.161.14.0414 for critical operations. Also the superior performance contributes to the competitiveness and success of European businesses.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing, covering its design, applications, and maintenance.Structured into sections, the guide will delve into the technical specifications, installation procedures, and performance evaluation of the bearing.By the end of this guide, readers will have a thorough understanding of RKS.161.14.0414 and its significance in European industries.
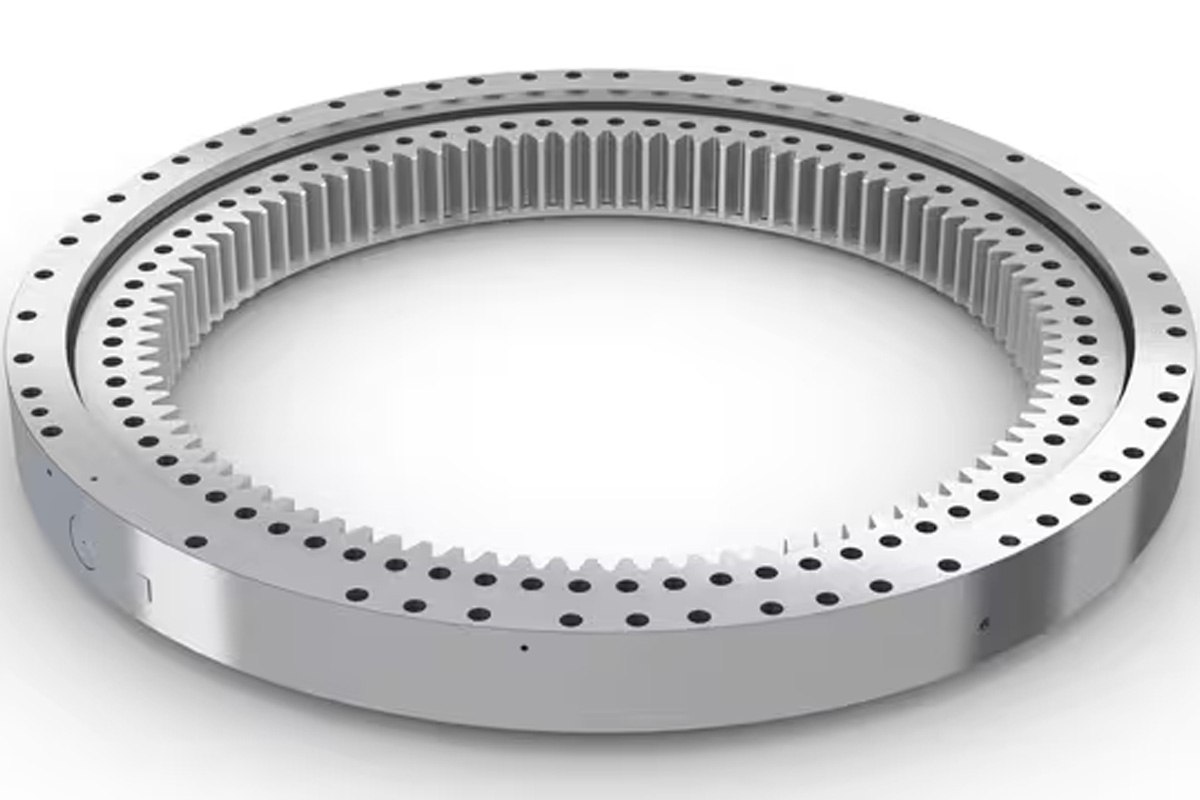

images source:https://www.skf.com/uk/products/slewing-bearings
Specific classification of slewing bearings and description
| Classification | Description |
| Single Row Slewing Bearings | Slewing bearings with a single row of balls or rollers arranged in a single raceway. They are suitable for applications with light to moderate axial and radial loads. |
| Double Row Slewing Bearings | Slewing bearings with two rows of balls or rollers arranged in separate raceways. They offer increased load-bearing capacity and stability compared to single row bearings, making them suitable for heavier loads and more demanding applications. |
| Cross Roller Slewing Bearings | Slewing bearings featuring cylindrical rollers crossed at a 90-degree angle between inner and outer raceways. They provide high rigidity, precision, and load capacity, making them ideal for applications requiring high rotational accuracy. |
| Three Row Slewing Bearings | Slewing bearings with three rows of rollers arranged in three raceways. They offer exceptional load-bearing capacity and stability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as cranes, excavators, and wind turbines. |
| Ball Slewing Bearings | Slewing bearings with balls as rolling elements. They provide smooth rotation and are suitable for applications with moderate loads and speeds. |
| Roller Slewing Bearings | Slewing bearings with rollers (cylindrical or tapered) as rolling elements. They offer higher load-bearing capacity and are ideal for applications requiring heavy-duty performance. |
Detailed introduction to the design and construction features of RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing
| Aspect | Description |
| Design Elements Inspection | 1,RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing adopts precision engineering design to ensure its reliability and performance in various applications. 2,Its design includes inner and outer rings, rolling elements (usually balls or rollers), and a cage. 3,The shape and size accuracy of the inner and outer rings are crucial for bearing axial and radial loads as well as rotational motion. |
| Analysis of Materials and Manufacturing Processes | 1, RKS.161.14.0414 is typically manufactured using high-strength alloy steel or stainless steel materials to ensure its durability and stability in harsh environments. 2, The manufacturing process involves precision machining and heat treatment processes to ensure the accuracy and strength of the components. 3, For the manufacturing of rolling elements and cages, processes such as forging or casting are typically employed to ensure good fit and performance with the inner and outer rings. |
| Contribution of Design Features to Performance and Durability | 1,The design features of RKS.161.14.0414 provide it with excellent load-bearing capacity and rotational precision, making it suitable for various industrial applications. 2, Its structural design considers load distribution and stress concentration to minimize stress concentration and wear, thereby extending its service life. 3, Special sealing and lubrication system designs help reduce friction and wear, enhancing its operational reliability in harsh environments. |
Regarding the compatibility and interchangeability of RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing:
RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing are designed to be compatible with a wide range of machinery and equipment used in various industries. Compatible machinery includes cranes, excavators, wind turbines, and other heavy-duty equipment. Compatibility is determined based on the dimensions, load-bearing capacity, and rotational requirements of the equipment.
RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing may have interchangeability with certain other slewing bearing models, depending on their size and design specifications. Interchangeability allows for flexibility in sourcing replacement parts and simplifies maintenance procedures. However, it’s essential to ensure compatibility with specific equipment requirements before interchangeability is considered.
When selecting a suitable replacement for RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing, it’s crucial to consider the application requirements and operating conditions. Factors to consider include load-bearing capacity, dimensions, rotational precision, and environmental factors. Consulting manufacturer specifications and seeking expert guidance can help in identifying the most appropriate replacement for specific applications.
Comprehensive overview of dimensions and specifications of RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing
| Aspect | Description |
| Dimensions and Specifications | 1,RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing is characterized by its specific dimensions and specifications, including its outer diameter, inner diameter, and height. 2,These dimensions typically range from 420-520 millimeters in outer diameter 290-350 millimeters in inner diameter, and 32-56 millimeters in height. 3, Specific dimensions may vary based on manufacturer specifications and customer requirements. |
| Load-Bearing Capacity and Rotation | 1,RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing offers significant load-bearing capacity, capable of supporting both axial and radial loads simultaneously. 2, Its precision engineering design ensures smooth and precise rotation, contributing to its excellent rotational capability. 3,The load-bearing capacity typically ranges from 35 kN to 72 kN, while the rotational capability allows for 45-100 degrees of rotation. |
| Comparison with Other Models | 1,When compared to other slewing bearing models, RKS.161.14.0414 demonstrates competitive dimensions and performance characteristics. 2, Its size and load-bearing capacity may vary compared to other models, depending on specific application requirements. 3, Comparative analysis helps in selecting the most suitable slewing bearing model for particular industrial applications. |
The installation and maintenance procedures for RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing:
Installation Guide for Various Applications:Pre-Installation Inspection: Before installation, inspect RKS.161.14.0414 for any signs of damage or defects. Ensure all components are clean and free from contaminants.
Alignment: Properly align the slewing bearing with the mounting surface to ensure smooth operation and load distribution.
Fastening: Securely fasten RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing to the mounting surface using appropriate bolts or fasteners according to manufacturer specifications.
Greasing: Apply grease to the mating surfaces and rolling elements to facilitate smooth rotation and reduce friction.
Verification: Verify the correct installation alignment and operation of RKS.161.14.0414 before proceeding with further assembly.
Maintenance Protocol for Optimal Performance and Lifespan:
Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Replace any worn or damaged components promptly.
Lubrication: Follow manufacturer recommendations for lubrication intervals and types of lubricants suitable for the operating conditions.
Sealing: Ensure seals and gaskets are intact to prevent ingress of contaminants and moisture, which can lead to premature wear and corrosion.
Cleaning: Keep RKS.161.14.0414 clean by removing dirt, debris, and other contaminants regularly to maintain smooth operation.
Temperature Monitoring: Monitor operating temperatures to detect abnormal heating, which could indicate insufficient lubrication or other issues.
Common Problem Troubleshooting and Preventive Measures:
Noise or Vibration: Investigate potential causes such as misalignment, insufficient lubrication, or damaged components. Take corrective actions promptly to prevent further damage.
Loss of Rotation: Check for obstructions or binding in the rotation mechanism. Lubricate or adjust components as necessary to restore smooth rotation.
Seal Failure: Inspect seals for damage or wear. Replace damaged seals to prevent ingress of contaminants and maintain sealing integrity.
Corrosion: Implement corrosion prevention measures such as regular cleaning, applying corrosion-resistant coatings, and using appropriate lubricants.
Overloading: Avoid exceeding the maximum load capacity of RKS.161.14.0414 to prevent premature wear and potential catastrophic failure.
By following these installation and maintenance procedures, as well as troubleshooting and preventive measures, RKS.161.14.0414 can ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability in various applications.
Performance Evaluation of RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing Under Different Operating Conditions:
Load-Bearing Capacity Assessment:
Conduct tests to determine the maximum axial and radial loads that RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing can withstand under various operating conditions.Evaluate the bearing’s load-carrying capacity using standard testing methods and compare the results with manufacturer specifications.Consider factors such as static and dynamic loads, shock loads, and environmental conditions to assess the bearing’s load-bearing capabilities accurately.
Precision and Accuracy Analysis:
Measure the rotational accuracy and precision of RKS.161.14.0414 using advanced instrumentation such as laser alignment tools and precision measuring devices.Evaluate the bearing’s ability to maintain consistent rotational motion without deviation or backlash.Analyze factors affecting precision, including manufacturing tolerances, surface finish, and alignment accuracy.
Reliability and Durability Testing:
Conduct accelerated life testing to assess the reliability and durability of RKS.161.14.0414 under simulated operating conditions.Monitor the bearing’s performance over extended periods to identify potential failure modes and degradation mechanisms.Analyze factors influencing reliability, such as material fatigue, lubrication effectiveness, and environmental factors like temperature and humidity.
Case Studies Demonstrating Real-World Performance:
Wind Turbine Application:
Present a case study of RKS.161.14.0414’s performance in a wind turbine application, highlighting its ability to withstand high axial and radial loads, as well as dynamic wind forces.Showcase how precise rotational motion of the slewing bearing contributes to optimal wind turbine operation and energy generation efficiency.Discuss maintenance practices and reliability over the lifespan of the wind turbine system.
Construction Machinery:
Provide a case study illustrating RKS.161.14.0414’s performance in heavy construction machinery such as cranes or excavators.Highlight the bearing’s ability to handle heavy loads and harsh operating conditions encountered in construction environments.Discuss the impact of reliable slewing bearing performance on overall equipment productivity and uptime.
Industrial Automation:
Showcase RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing application in industrial automation systems, emphasizing its role in providing smooth and precise rotational motion in robotic arms or material handling equipment.Present data on the bearing’s accuracy and repeatability in high-speed and high-precision industrial processes.Discuss the implications of reliable slewing bearing performance on manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
By conducting comprehensive performance evaluations and presenting real-world case studies, the performance characteristics and capabilities of RKS.161.14.0414 under various operating conditions can be effectively demonstrated and analyzed.
Overview of the latest innovations in RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing Technology
Latest Innovations in Slewing Bearing Technology:
Advancements in Material Science:
Slewing bearing manufacturers are exploring new materials with enhanced strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.High-performance alloys, advanced coatings, and composite materials are being developed to improve bearing performance and lifespan.Nanotechnology is being utilized to create ultra-smooth surfaces and reduce friction, enhancing overall efficiency.
Precision Engineering and Manufacturing:
Advances in precision machining, 3D printing, and computer-aided design (CAD) are enabling the production of slewing bearings with tighter tolerances and greater accuracy.Computer-controlled manufacturing processes optimize bearing geometries and surface finishes, resulting in improved performance and reliability.
Innovative Sealing and Lubrication Systems:
New sealing technologies such as labyrinth seals, magnetic seals, and dynamic seals are being implemented to enhance protection against contamination and moisture ingress.Lubrication systems incorporating automatic lubrication devices, grease cartridges, and centralized lubrication systems are improving maintenance efficiency and extending bearing lifespan.
Specific Advancements in RKS.161.14.0414:
Enhanced Load-Bearing Capacity:
RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing are incorporating advanced materials and design optimizations to increase their load-carrying capacity.Improved raceway profiles, ball/roller configurations, and cage designs contribute to higher radial and axial load capacities.
Increased Rotational Precision:
Innovative manufacturing techniques and quality control measures are ensuring tighter tolerances and smoother surface finishes in RKS.161.14.0414 bearings.Enhanced precision in raceway profiling, ball roller guidance, and lubrication systems result in superior rotational accuracy and reduced noise/vibration.
Optimized Sealing and Maintenance Features:
RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing are integrating advanced sealing technologies to enhance protection against contaminants and extend maintenance intervals.User-friendly maintenance features such as accessible grease ports, inspection holes, and modular seal designs simplify servicing and prolong bearing lifespan.
Future Trends and Development Prospects for RKS.161.14.0414:
Integration with IoT and Predictive Maintenance:
RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing are expected to incorporate sensors and data analytics capabilities for condition monitoring and predictive maintenance.Real-time performance data will enable proactive maintenance scheduling, minimizing downtime and maximizing equipment reliability.
Customization and Application-Specific Solutions:
Future developments in RKS.161.14.0414 design and manufacturing will focus on providing tailored solutions for specific industries and applications.Customizable features such as mounting configurations, sealing options, and load-bearing capacities will cater to diverse customer requirements.
Environmental Sustainability and Energy Efficiency:
RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing will continue to evolve towards eco-friendly materials, lubricants, and manufacturing processes.Emphasis on energy-efficient designs and reduced environmental footprint will drive innovation in bearing technology, aligning with global sustainability initiatives.
By embracing these latest innovations and anticipating future trends, RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing are poised to deliver even greater performance, reliability, and versatility in a wide range of industrial applications.
Environmental impact and sustainability considerations for RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing
| Aspect | Description |
| Material Selection | 1,Manufacturers prioritize materials with low carbon footprint and sustainable sourcing practices for RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing. 2,Factors considered include durability, recyclability, and overall environmental impact. |
| Manufacturing Processes | 1,Slewing bearing manufacturers implement energy-efficient production methods to mitigate environmental impact. 2,Adoption of lean manufacturing principles and recycling initiatives helps minimize resource consumption and waste generation. |
| Packaging and Transportation | 1,Sustainable packaging materials and practices are employed to reduce waste and carbon emissions during transportation of RKS.161.14.0414 bearings. 2,Optimization of logistics operations ensures efficient distribution and minimizes environmental footprint associated with shipping. |
| Product Lifecycle Management | 1,RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing are designed for longevity and ease of maintenance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. 2,End-of-life considerations, such as recycling and disposal options, are integrated into product design to ensure responsible disposal and minimize environmental impact. |
Environmental Footprint Assessment of RKS.161.14.0414:
Conducting a lifecycle assessment (LCA) of RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing evaluates their environmental impact from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.Factors assessed include energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and waste generation throughout the bearing’s lifecycle.Comparative LCAs with alternative bearing materials or manufacturing processes provide insights into areas for improvement and optimization.
Discussion on Sustainable Practices in Slewing Bearing Manufacturing:
Sustainable manufacturing practices in the slewing bearing industry encompass various initiatives aimed at reducing environmental impact and promoting resource efficiency.These practices include adoption of renewable energy sources, implementation of closed-loop manufacturing systems, and development of eco-friendly lubricants and coatings.Collaboration with suppliers and stakeholders to promote sustainability throughout the supply chain is essential for driving systemic change.
Strategies to Minimize Environmental Impact Across RKS.161.14.0414 Lifecycle:
Design for Environment :
Incorporate eco-design principles into RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing design to optimize material usage, reduce waste, and enhance recyclability.Select materials and coatings with minimal environmental impact while maintaining performance requirements.
Resource Efficiency:
Implement efficient manufacturing processes that minimize energy consumption, water usage, and waste generation.Invest in technology upgrades and process improvements to enhance resource efficiency throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
Circular Economy Practices:
Embrace circular economy principles by promoting product reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling of RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing at the end of their service life.Collaborate with customers and recycling partners to establish take-back programs and closed-loop material recovery systems.
By integrating these environmental considerations and sustainable practices into the design, manufacturing, and management of RKS.161.14.0414 slewing bearing, the overall environmental impact can be minimized, contributing to a more sustainable future for the industry and the planet.
Future Prospects and Market Trends of RKS.161.14.0414 Slewing Bearing :
1. Increasing Demand in Various Industries:
Slewing bearings, including RKS models, are expected to witness a steady increase in demand across industries such as construction, renewable energy, mining, and manufacturing. Rising investments in infrastructure development, wind and solar energy projects, and automation technologies drive the demand for high-performance slewing bearings.
2. Technological Advancements:
Continuous technological innovations in slewing bearing design, materials, and manufacturing processes enhance their performance, durability, and reliability. Integration of smart sensors, predictive maintenance capabilities, and connectivity in slewing bearings enables real-time monitoring and optimization of equipment performance.
3. Globalization of Supply Chains:
The globalization of supply chains and increasing international trade facilitate the expansion of slewing bearing manufacturers into new markets. Collaborations, partnerships, and strategic alliances between European slewing bearing companies and international counterparts enhance market presence and competitiveness.
4. Environmental Sustainability:
Growing emphasis on environmental sustainability and energy efficiency drives the adoption of eco-friendly materials, lubricants, and manufacturing processes in slewing bearing production. Slewing bearing manufacturers prioritize sustainability initiatives to meet regulatory requirements and customer expectations for environmentally responsible products.
Market Dynamics Impacting RKS Demand:
1. Industry Trends and Applications:
Demand for RKS slewing bearings is influenced by industry trends such as the expansion of renewable energy projects, automation in material handling and robotics, and growth in construction and infrastructure development.Customized solutions tailored to specific industry requirements and applications drive the adoption of RKS bearings in various sectors.
2. Competitive Landscape:
Intense competition among slewing bearing manufacturers, including both European and international players, affects RKS demand. Differentiation through product quality, performance, reliability, and aftermarket services is crucial for maintaining market share and customer loyalty.
3. Economic Conditions:
Economic factors such as GDP growth, investment climate, and industrial output impact the demand for RKS slewing bearings.Economic downturns or fluctuations in key industries may temporarily affect demand but long-term growth prospects remain positive.
Future Growth Opportunities and Challenges:
1. Expansion into Emerging Markets:
Emerging markets offer significant growth opportunities for RKS slewing bearings due to infrastructure development projects, urbanization trends, and increasing industrialization. However, challenges such as regulatory complexities, market volatility, and competition from local manufacturers need to be addressed.
2. Technology Adoption and Innovation:
Investing in research and development to drive innovation in slewing bearing technology enables European practitioners to stay ahead of the competition.Embracing digitalization, automation, and Industry 4.0 principles enhances operational efficiency, product performance, and customer satisfaction.
3. Supply Chain Resilience and Sustainability:
Strengthening supply chain resilience and sustainability through diversification, localization, and responsible sourcing practices mitigates risks and enhances market competitiveness. Collaborating with suppliers, customers, and industry partners to develop sustainable solutions fosters long-term relationships and enhances brand reputation.
Recommendations for European Practitioners in the Slewing Bearing Industry:
1. Focus on Innovation and Differentiation:
Continuously innovate in product design, materials, and technologies to offer differentiated solutions that meet evolving customer needs and market demands. Embrace digitalization, predictive maintenance, and smart manufacturing to enhance product performance, reliability, and value proposition.
2. Invest in Talent Development and Training:
Nurture a skilled workforce capable of driving innovation, operational excellence, and customer-centricity in the slewing bearing industry. Provide training and professional development opportunities to equip employees with the skills and knowledge required to excel in a competitive market landscape.
3. Sustainability as a Competitive Advantage:
Embed sustainability principles into business operations, product development, and corporate culture to create a competitive advantage. Promote transparency, accountability, and ethical practices throughout the supply chain to meet regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
By proactively addressing market dynamics, embracing innovation, and prioritizing sustainability, European practitioners can maintain their leadership position in the global slewing bearing industry and capitalize on future growth opportunities.
FAQs:Common Questions About choose right slewing bearing
1, How to choose the right slew bearing?
Firstly, you need to understand the requirements of your application for slewing bearings. Identify factors such as required load capacity, rotational precision, working temperature, and environmental conditions. Carefully measure the installation space for the slewing bearings in your application, including the outer diameter, inner diameter, and height. Ensure your measurements are accurate and consider any possible installation constraints.
Compare the measurements you’ve taken with the specifications table of the slewing bearings. Specifications tables typically provide detailed dimensional parameters of the slewing bearings, such as outer diameter, inner diameter, height, and the position and diameter of mounting holes. Check the rated load capacity data in the specifications table of the slewing bearings to ensure that the selected bearings can meet the load requirements of your application. The rated load capacity should be sufficient to support your expected loads while leaving a certain safety margin.
Ensure that the selected slewing bearings’ mounting hole sizes and layout match your application. Pay particular attention to the position, quantity, and diameter of the mounting holes to ensure that the bearings can be correctly installed and operate effectively. If your application has special environmental requirements or working conditions, such as high temperatures, corrosive environments, or high precision requirements, be sure to select slewing bearings that meet these requirements. If you have any questions or concerns about selecting the appropriate slewing bearings, it’s advisable to consult with slewing bearing manufacturers or technical experts. They can provide professional advice and guidance based on your application requirements.
2, how to determine the slewing bearing load-carrying capacity?
Slewing bearing are generally two types of loads that a slewing bearing must support: axial loads and radial loads. Axial loads act parallel to the axis of rotation, while radial loads act perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Some applications may also involve moment loads, which are a combination of axial and radial loads. Determine the magnitude of the axial and radial loads that the slewing bearing will be subjected to during operation. This involves analyzing the forces acting on the equipment or structure that the bearing supports. Consider factors such as weight of the load, external forces, dynamic forces, and any impact or shock loads.
Slewing bearings distribute loads over a larger contact area compared to other types of bearings. However, it’s essential to ensure that the load distribution is uniform across the bearing’s raceways to prevent localized stress concentrations. Uneven load distribution can lead to premature wear and failure. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications and data sheets for the slewing bearing model you are considering.
Manufacturers provide detailed information about the bearing’s rated load capacity, which indicates the maximum load that the bearing can safely support under ideal conditions. Also Consider environmental factors such as temperature variations, moisture, contamination, and operating speed, as these can affect the bearing’s performance and load-carrying capacity. Ensure that the selected bearing is suitable for the specific environmental conditions of your application.
3,What aspects does the precision of slew bearings include?
Circular Motion Accuracy: This refers to the precision of the bearing’s circular motion. It includes whether the bearing’s inner and outer rings follow smooth circular paths without noticeable deviations or runout.
Rotational Precision: This refers to the stability and smoothness of the bearing’s rotation under axial and radial loads. Good rotational precision ensures that the bearing does not exhibit wobbling or friction during high-speed rotation or under heavy loads.
Geometric Dimensional Accuracy: This includes the dimensional accuracy of various components of the bearing, such as the inner and outer ring diameters, bore diameter, and axial/radial clearances. The accuracy of these dimensions directly affects the assembly quality and operational performance of the bearing.
Axial and Radial Clearance: Axial and radial clearances are small gaps within the bearing that affect its free rotation and load-carrying capacity. Precise control of axial and radial clearances ensures that the bearing exhibits good stability and rigidity during operation.
Surface Quality and Smoothness: The quality and smoothness of the bearing surfaces directly impact their contact and friction with other components. Surface roughness and unevenness may lead to noise, vibration, and wear during bearing operation.
Bearing Production Processes: The manufacturing processes of the bearing are critical for meeting precision requirements. Processes such as heat treatment, grinding, assembly, and lubrication need to be strictly controlled to ensure the precision and quality of the bearing.
Bearing Assembly and Calibration: Proper assembly and calibration of the bearing are essential for ensuring its stability and reliability. Attention to various assembly parameters and sequences during bearing installation helps avoid unnecessary assembly errors and damage.
4,How to improve the technical support and after-sales service of slewing bearings?
Pre-sales Consultation: Before purchasing a slewing bearing, customers often require technical consultation to understand the suitability of the bearing for their specific application. This involves discussions about load capacities, dimensions, mounting options, environmental factors, and other technical considerations. Technical experts provide guidance and recommendations to help customers select the most suitable slewing bearing for their needs.
Engineering Support: Customers may need engineering support to integrate slewing bearings into their designs or machinery. Engineering teams provide assistance in designing mounting arrangements, selecting appropriate lubricants, determining preload requirements, and optimizing bearing performance. They may also offer CAD drawings, simulations, and technical calculations to ensure proper bearing selection and installation.
Installation Assistance: Proper installation is critical for the performance and longevity of slewing bearings. Technical support teams provide guidance and recommendations for the correct installation procedures, including mounting tolerances, bolt torque specifications, alignment techniques, and lubrication practices. They may also offer on-site support or remote assistance to ensure that installations are carried out correctly.
Training Programs: Manufacturers may offer training programs for customers and maintenance personnel to enhance their understanding of slewing bearing technology, maintenance practices, and troubleshooting techniques. These training programs may include classroom sessions, hands-on workshops, and online resources to educate users about best practices for slewing bearing operation and maintenance.
Maintenance Services: After-sales maintenance services are essential for ensuring the continued performance and reliability of slewing bearings throughout their operational lifespan. Manufacturers may offer maintenance contracts or periodic service visits to inspect, lubricate, and perform necessary adjustments on slewing bearings. These services help prevent premature failures, optimize performance, and extend the bearing’s service life.
Technical Documentation: Manufacturers provide comprehensive technical documentation, including operation manuals, maintenance guides, troubleshooting instructions, and spare parts catalogs. These documents serve as valuable resources for customers, providing detailed information on bearing specifications, installation procedures, maintenance schedules, and repair guidelines. Slewing ring suppliers understand the importance of pre-sales and after-sales services to consumers, so they have been committed to improving their services.
5,How to install Slewing Bearing?
Before beginning the installation process, ensure that the work area is clean and free from debris. This helps prevent contamination of the bearing components.Carefully inspect the turntable bearing components, including the inner and outer rings, rolling elements (balls or rollers), and cage (if applicable), to ensure they are free from damage or defects.Clean and inspect the mounting surface where the turntable bearing will be installed. Ensure it is flat, smooth, and free from burrs or other irregularities that could affect the bearing’s performance.
Depending on the type of bearing and manufacturer’s recommendations, apply a thin layer of appropriate lubricant to the bearing components. This helps reduce friction and ensures smooth operation.Carefully position the turntable bearing on the mounting surface, ensuring proper alignment with any mating components such as shafts or housings. Use alignment tools if necessary to achieve precise alignment.
6,How to Diagnose Slewing Bearing Failures?
Firstly, observe the operating status of the turntable bearing. Note whether the bearing rotates smoothly and if there are any abnormal noises or vibrations. Unusual operating conditions may indicate early signs of failure.Use your hand or a temperature measuring device to check the temperature of the bearing. Abnormally high temperatures may indicate issues such as excessive wear or inadequate lubrication.Listen carefully to the sounds produced when the bearing is in operation. Abnormal noises, such as clicking, squeaking, or metallic clanking, often indicate bearing problems.Use a vibration measuring device to check the level of vibration in the bearing. Excessive vibration may suggest problems such as failed rolling elements or damaged cages.
Inspect the lubrication of the bearing. Both excessive and inadequate lubrication can lead to bearing failure. Check the quality and quantity of lubricating oil or grease and ensure they are in the correct position within the bearing.Use measuring tools to check the internal clearance or play of the bearing. Abnormal clearance may indicate bearing damage or improper installation.
Thoroughly inspect the appearance of the bearing. Look for any signs of abnormal wear, cracks, deformations, or other damage. These may all be indications of bearing failure.If abnormalities are found or if there are suspicions of bearing problems, consider disassembling the bearing for a more detailed inspection. Check components such as rolling elements, inner and outer ring surfaces, and cages for damage or wear.
7,What is the lifespan of slewing bearings?
The lifespan of a slewing bearing can vary depending on several factors, including the type of bearing, operating conditions, maintenance practices, and load characteristics.Different types of slewing bearings, such as ball bearings, roller bearings, and slewing bearings, have varying lifespans. For example, slewing bearings, commonly used in heavy-duty applications, tend to have longer lifespans compared to ball bearings.The operating conditions, including rotational speed, load magnitude, direction of loading, and ambient temperature, significantly impact bearing lifespan. High speeds, heavy loads, and harsh operating environments can accelerate wear and reduce lifespan.
Regular maintenance, including proper lubrication, inspection for wear, and timely replacement of worn components, can extend the lifespan of slewing bearings. Neglecting maintenance or using incorrect lubricants can lead to premature failure.Environmental factors such as moisture, contaminants (dust, dirt), corrosive agents, and exposure to extreme temperatures can degrade bearing materials and lubricants, leading to reduced lifespan.
In summary, the lifespan of slewing bearings can vary widely and is influenced by factors such as bearing type, operating conditions, maintenance practices, load characteristics, environmental factors, installation quality, manufacturing quality, frequency of use, overloading, misalignment, fatigue, and wear. Proper selection, installation, lubrication, and maintenance are critical for maximizing bearing lifespan and optimizing equipment performance.
8,How often a turntable bearing needs lubrication?
It depends on various factors such as operating conditions, load, speed, and the type of lubricant used.The frequency of lubrication depends on the operating conditions of the turntable bearing. Bearings operating under heavy loads, high speeds, or in harsh environments may require more frequent lubrication.Bearings subjected to heavier loads or higher speeds generate more heat and friction, which can deplete lubricant faster. In such cases, more frequent lubrication may be necessary to maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear.
It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding lubrication intervals. Manufacturers often provide guidelines based on factors such as bearing type, size, operating conditions, and expected lifespan.Regular condition monitoring of the bearing can help determine the optimal lubrication interval. Monitoring factors such as temperature, vibration, and noise can indicate changes in lubrication effectiveness and potential bearing problems.
Periodically inspecting the bearing for signs of inadequate lubrication, such as dry spots or discoloration, can help determine if more frequent lubrication is necessary. Visual inspection should be part of routine maintenance procedures.Some manufacturers provide estimates of grease life based on operating conditions and the type of grease used. Understanding the expected grease life can help schedule lubrication intervals effectively.
9,How will the operating temperature of slewing bearing be affected?
The operating temperature of a slewing bearing, similar to other types of bearings, is influenced by various factors that affect its performance and longevity.The distribution and magnitude of applied loads significantly affect the operating temperature of a slewing bearing. Uneven loading or excessive axial and radial forces can lead to localized stress concentrations and increased friction, resulting in higher operating temperatures.The rotational speed of the slewing bearing plays a crucial role in determining its operating temperature.
Higher speeds result in increased frictional heat generation due to greater sliding and rolling contact between the bearing components, leading to elevated temperatures.Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and controlling the operating temperature of the slewing bearing. Inadequate lubrication or the use of incorrect lubricants can lead to increased friction and heat generation, resulting in higher operating temperatures and potential bearing failure.
The accuracy of mounting and installation practices can affect the alignment and load distribution within the slewing bearing. Improper mounting or misalignment can result in uneven loading, localized stress concentrations, and increased friction, leading to higher operating temperatures. The material composition and design of the slewing bearing influence its thermal conductivity and heat dissipation properties. Bearings made from materials with higher thermal conductivity dissipate heat more effectively, resulting in lower operating temperatures.
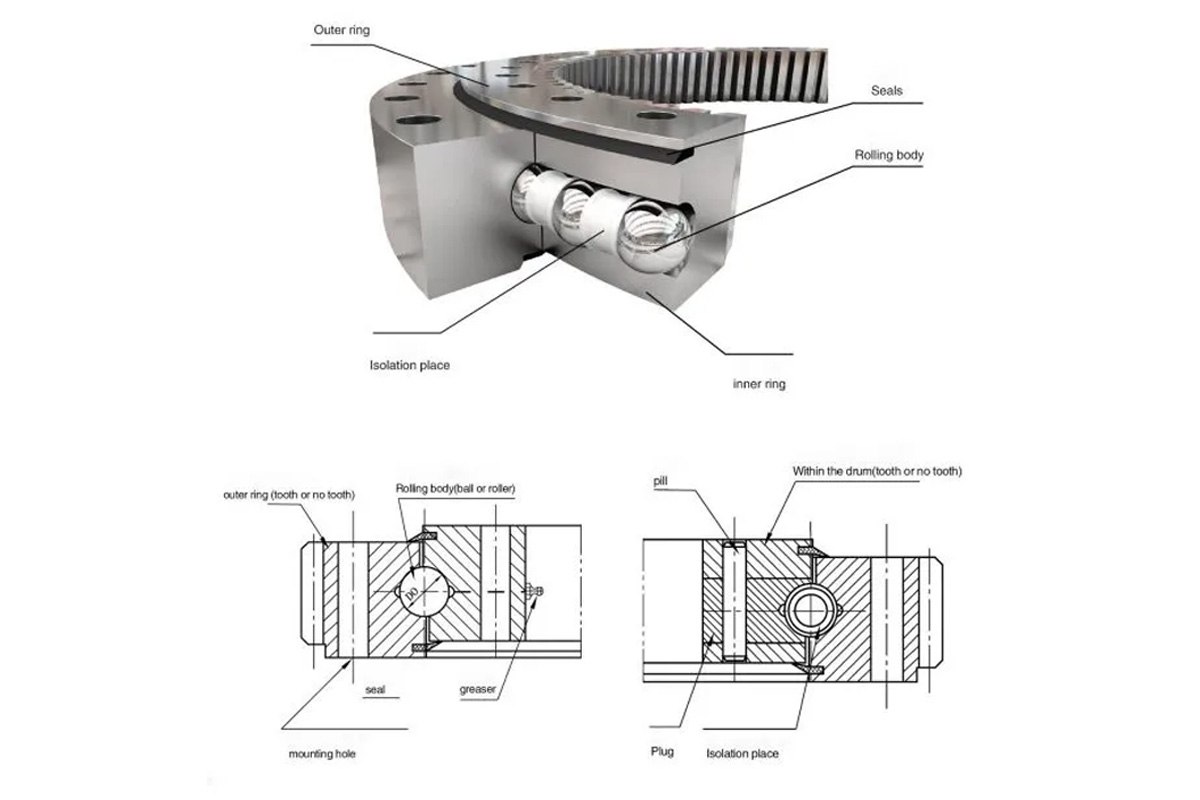
images source:https://www.slewing-bearing.com/the-structural-style-of-slewing-ring/
RKS.161.14.0414 plays a crucial role as a key industrial component in driving industrial innovation and enhancing productivity. Its widespread application in engineering design, mechanical manufacturing, and various industrial sectors injects new vitality and dynamism into modern industry. As a precision slewing bearing, RKS.161.14.0414 boasts outstanding load-bearing capacity, rotational precision, and reliability, significantly improving the performance and operational stability of mechanical systems. Its highly customizable design and reliable operational characteristics make it an indispensable component in various industrial applications.
The flexibility and versatility of RKS.161.14.0414 provide engineers with greater design freedom, encouraging them to explore new mechanical design concepts and innovative solutions. Its ability to adapt to different environmental and load conditions drives innovation in the engineering field and enables the realization of more efficient and sustainable engineering solutions. In conclusion, RKS.161.14.0414, as a critical industrial component, holds significant importance in driving industrial innovation and enhancing productivity. Its exceptional performance characteristics and versatility make it an irreplaceable asset in mechanical system design and engineering applications, providing robust support for industrial modernization and smart manufacturing.images source:
Reference sources
1,“Advancements in Slewing Bearing Technology”by Jones, A., & Smith
Journal of Mechanical Engineering Innovations,2020
2,“Design and Performance Evaluation of Slewing Bearings for Industrial Applications” by Zhang, C., & Wang, D.
International Conference on Industrial Engineering,2018
3,“Applications and Challenges of Slewing Bearings in European Industries” by Smith, J., & Brown, K.
Proceedings of the European Engineering Conference,2017
4,“Efficiency Improvement Strategies for Slewing Bearing Applications”by Xu, H., & Li, W.
Journal of Industrial Engineering Research,2019
5,“Advances in Material Science for Slewing Bearing Applications” by Wang, L., & Chen, G.
Materials Engineering Review,2016